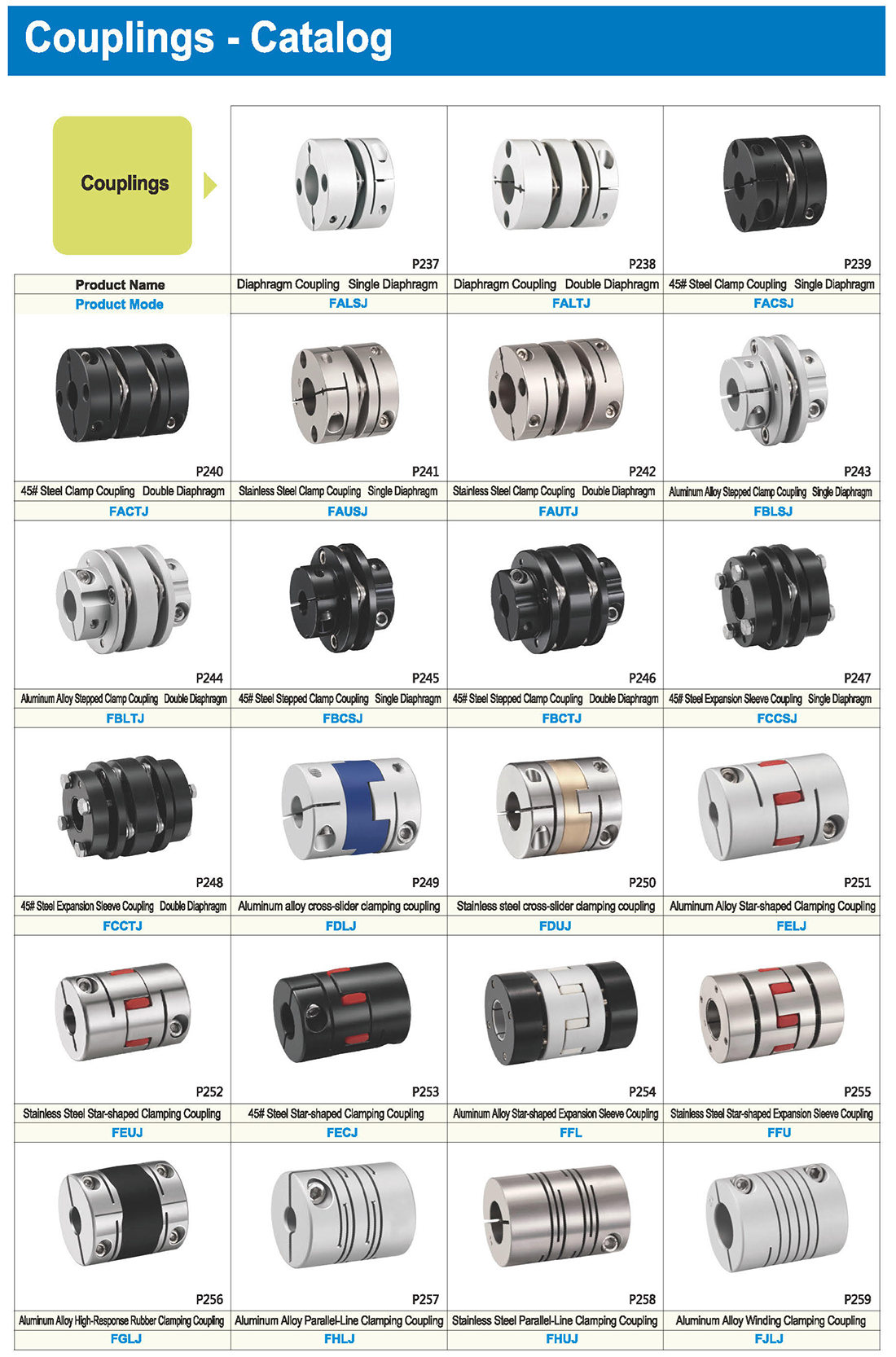
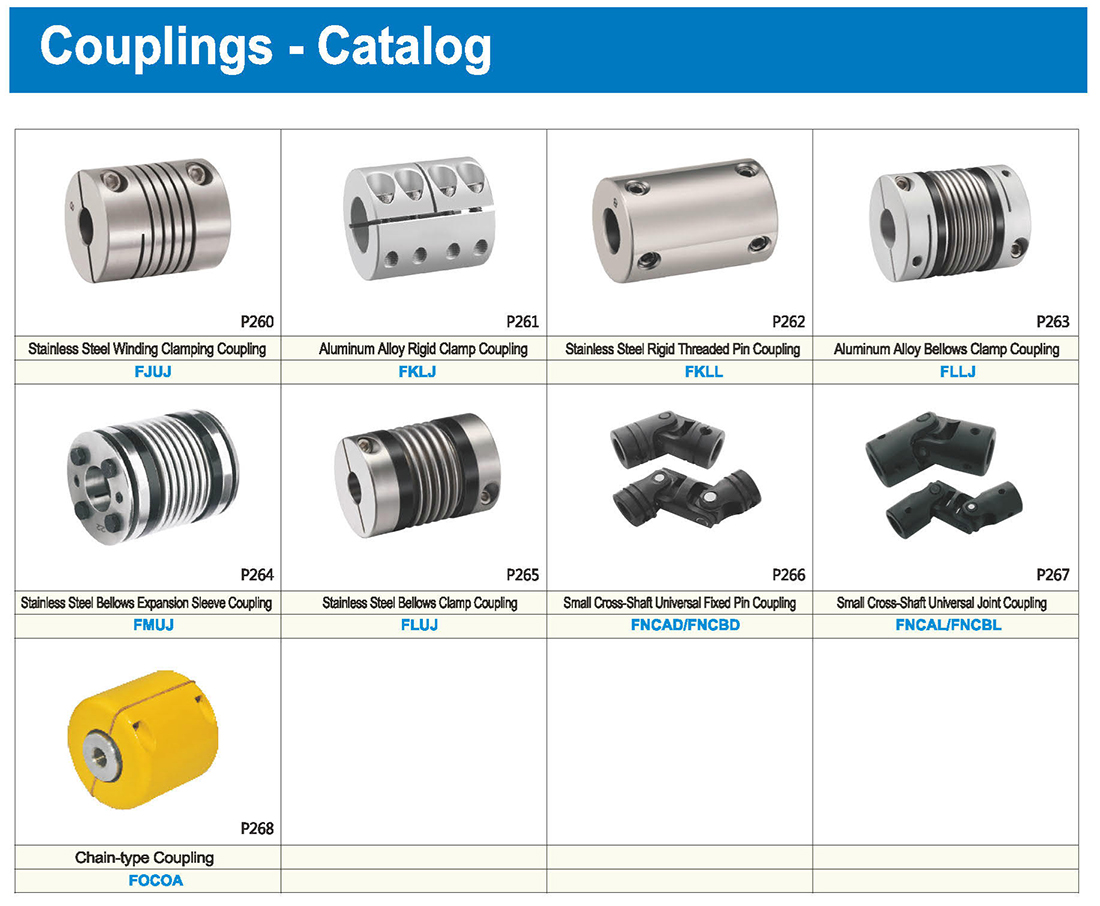
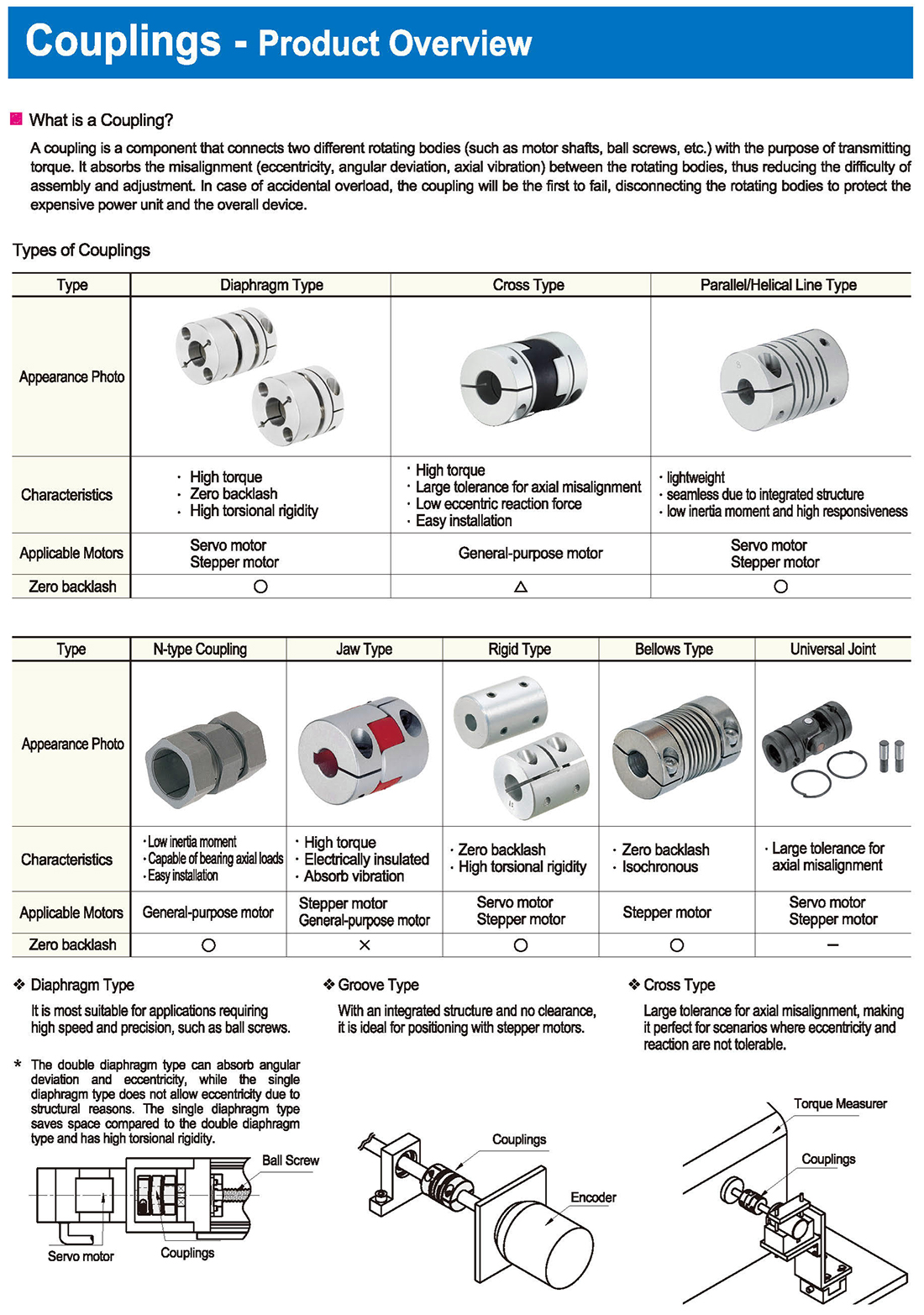
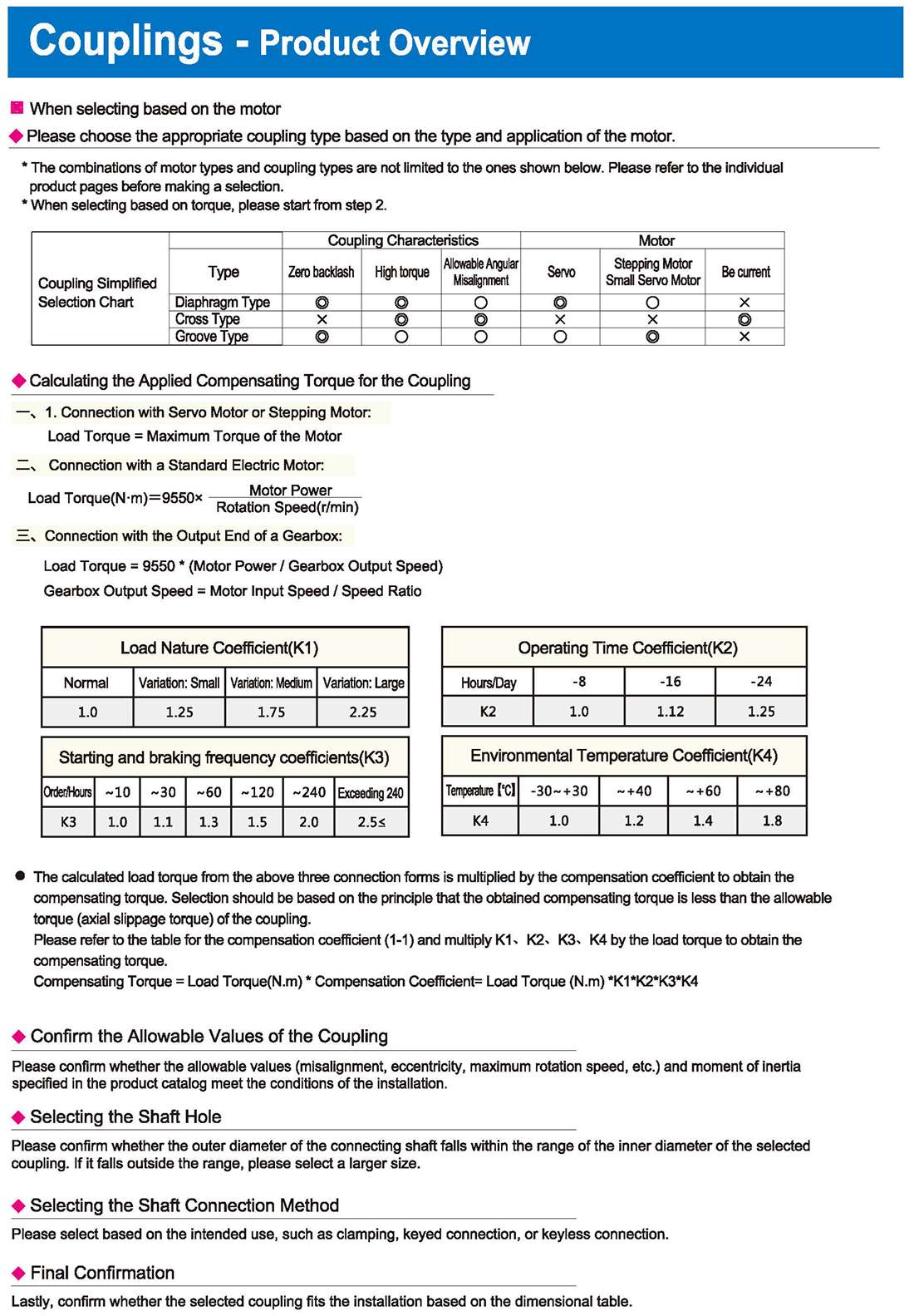
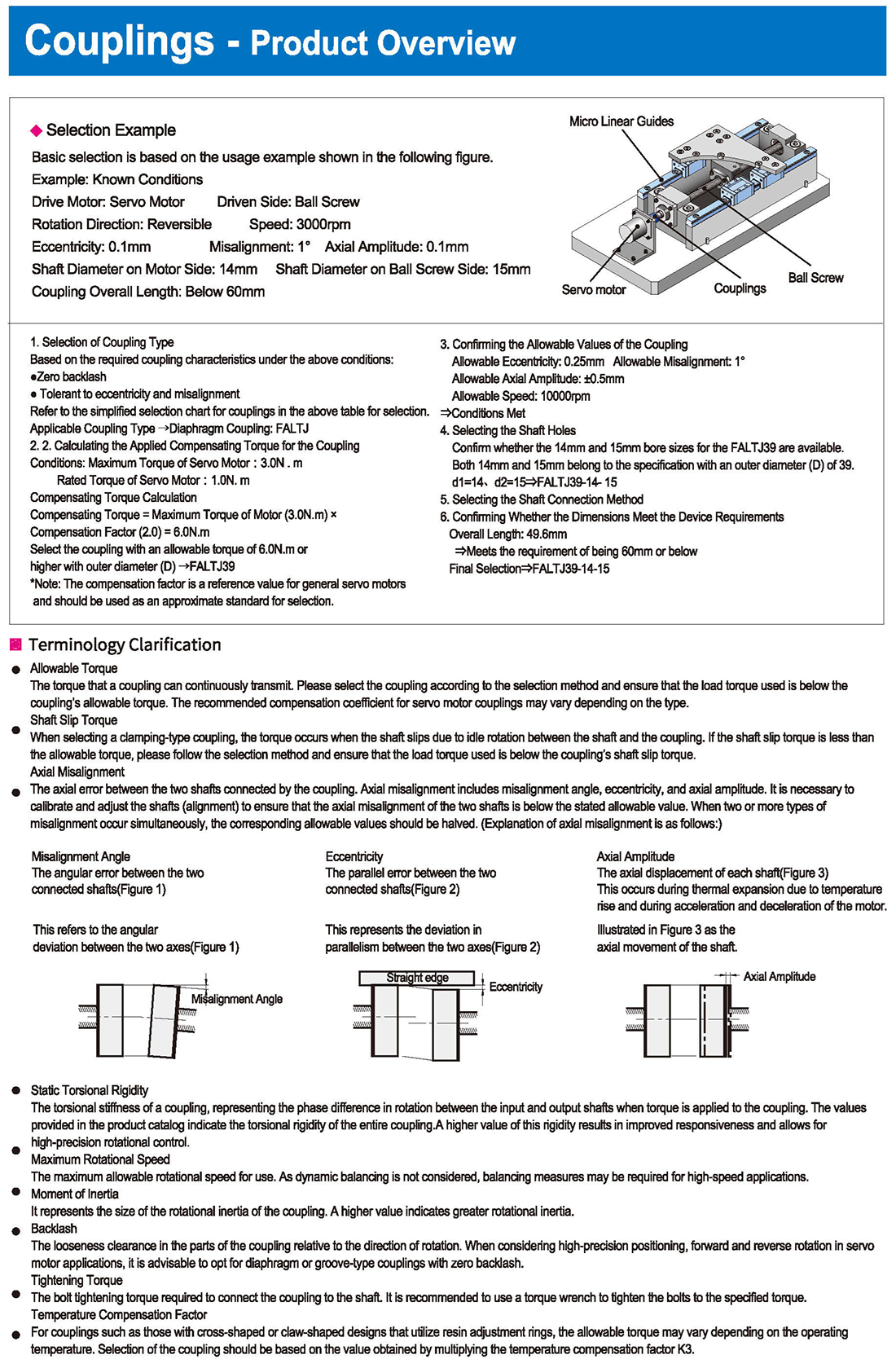
-
-
Коробка передач под прямым углом 90 градусов
- Aatm-как точное рулевое устройство серии
- Точное рулевое устройство серии AAT-AS
- Точность серии 90 градусов
- Pt-стандартное рулевое устройство серии
- Серия точных 90 - градусного редуктора
- На входном рулевом устройстве оси серии
- Фланцевый вход серии AT-F 90 - градусный редуктор
- Синхронный винтовой лифт серии RB
- Классический планетарный вклад кно в управление
- CCT классический вход в шахту руля
-
-
-
-
- Руль для рук
- - с ручкой
- Различные типы ручек
- Штырь/штырь
- В центре города
- Категория защиты от ударной абсорбции
- Пневматические зажимы/быстрые зажимы
- Размещение деталей/направляющих частей
- Фиксатор/фиксатор позиционирования
- Мелкие детали/магнит
- Монтажные опоры/основания/крепления
- Соединительный блок
- Пневматические аксессуары и аксессуары
- Выравнивание ступней ног
- 3. Дверные замки
- Потяни за ручку.
- - петель
-
На электродвигателе
- Электродвигатель с открытым контуром + электродвигатель с закрытым контуром + винтовой шаговый электродвигатель
- Водитель автомобиля степпер (открытая/закрытая петля)
- Серводвигатель переменного тока + водитель серводвигателя переменного тока
- Серводвигатель постоянного тока + водитель серводвигателя постоянного тока (импульсный + тип шины)
- Двигатель постоянного тока без щетки и драйвер постоянного тока без щетки
- Прямой привод DD motor + линейный двигатель
- ПЛК программируемый контроллер/контроллер движения (карточная/визуальная система управления все в одном устройстве)
- Взрывозащищенный специальный двигатель


 Английский язык
Английский язык Русский язык
Русский язык На испанском языке
На испанском языке На итальянском языке
На итальянском языке Арабский язык
Арабский язык Корейская народно-демократическая республика
Корейская народно-демократическая республика Немецкий язык
Немецкий язык На японском языке
На японском языке На вьетнамском языке
На вьетнамском языке На турецком языке
На турецком языке
 1. Введение
1. Введение Таблица технических характеристик
Таблица технических характеристик скачать
скачать